What Happens Inside an EMC Chamber? A Deep Dive into Its Functionality
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) testing is crucial for ensuring that electronic devices meet regulatory standards and operate properly without causing interference to other devices. The EMC chamber is one of the most specialized environments for performing these tests. This article will explore what happens inside a chamber, its purpose, and how it ensures that your device complies with the necessary regulations.
Understanding the Basics of an EMC Chamber
An EMC chamber is a controlled testing environment specifically designed to assess the electromagnetic emissions produced by electronic devices. This chamber plays a vital role in EMC testing by measuring both the emissions that the device produces and its susceptibility to external electromagnetic interference. The chamber's structure helps simulate real-world conditions while keeping external noise and interference to a minimum.
The Importance of EMC Testing
Electronic devices can generate electromagnetic emissions that interfere with the operation of other nearby devices. These emissions are part of the electromagnetic spectrum. When devices emit high levels of these waves, it can cause issues such as poor Wi-Fi performance, distorted TV signals, and, in some cases, even more severe interference in critical systems like medical equipment. EMC testing helps ensure that electronic products do not cause such interference, making compliance with regulations a vital step in the product development process.
Types of Chambers for EMC Testing
There are different types of EMC test chambers used for various testing purposes. The most common ones are semi-anechoic chambers, EMC anechoic chambers, and open-air testing sites.
-
Semi-Anechoic Chambers: These chambers are equipped with absorbent materials that prevent electromagnetic waves from reflecting off surfaces. They are designed for emissions testing.
-
EMC Anechoic Chambers: These are fully lined with materials that absorb electromagnetic waves, allowing for precise measurements of the device under test.
-
Open Area Test Sites (OATS): Although not as enclosed as chambers, OATS are used for testing devices in a more natural environment, usually outside, though they are less controlled than chambers.
How EMC Chambers Operate
The Role of Absorbent Materials
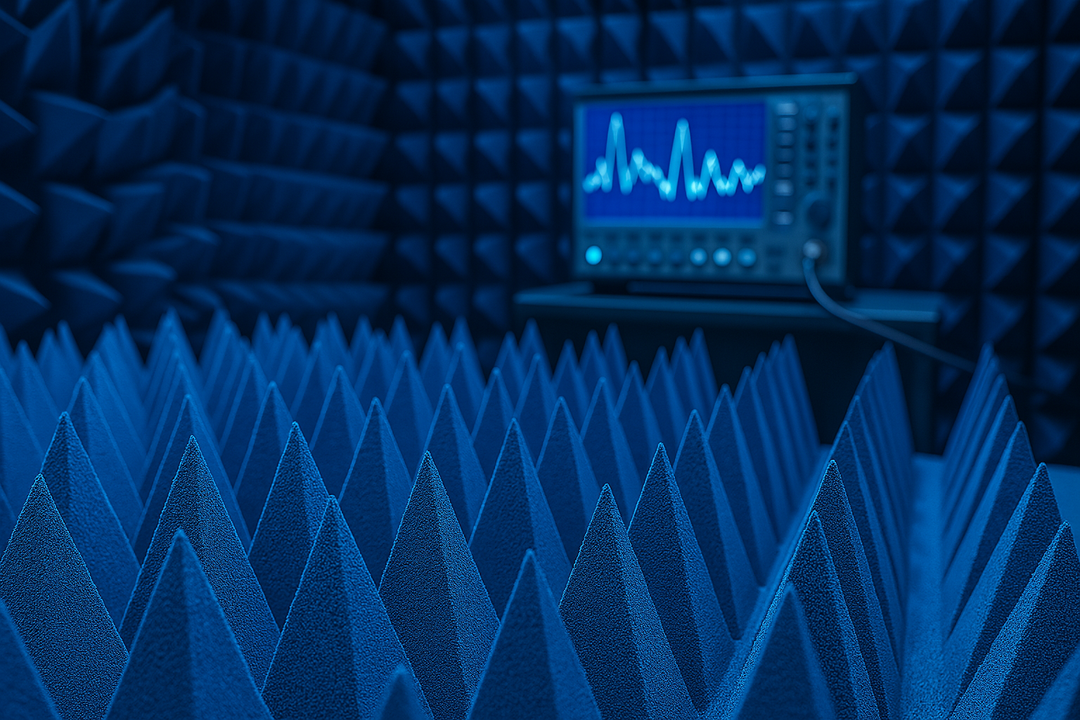
An essential component of an EMC anechoic chamber is the material used to absorb electromagnetic waves. These materials prevent reflections from distorting the test results. Typically, chambers are lined with ferrite tiles, RF foam absorbers, or a combination of both. The purpose of these materials is to mimic a "free-space" environment in which electromagnetic waves are not affected by surrounding structures.
The Test Setup
In an EMC test chamber, the device under test (DUT) is placed at a specific distance from antennas that are used to measure both emissions and immunity. The device is exposed to a controlled electromagnetic environment where the engineers assess how much electromagnetic interference the device produces, as well as how well it can withstand interference from other sources.
The EMC chamber is equipped with various sensors, antennas, and equipment that measure the electromagnetic fields emitted from the device. These measurements are crucial for determining whether the device meets the regulatory requirements set by governing bodies like the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the U.S. or the European Union's EMC Directive.
Testing for Immunity and Emissions
EMC testing can be divided into two main categories:
-
Emission Testing: This test measures the electromagnetic energy emitted by the device during operation. The goal is to ensure that the emissions are within allowable limits so that the device does not interfere with other electronic systems.
-
Immunity Testing: This test evaluates how well a device can resist electromagnetic interference from other devices. The device is deliberately exposed to electromagnetic waves from various sources to assess its resilience.
Compliance and Standards
Achieving Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Compliance with electromagnetic compatibility regulations is essential for devices intended for market release. In the United States, devices must comply with FCC Part 15 rules, while in Europe, they must meet the EMC and RED Directives. An EMC chamber is used to conduct the necessary tests to verify that a device adheres to these standards.
FCC Part 15 covers unintentional radiators (devices that emit radio frequency energy) and sets limits on the amount of electromagnetic radiation they can emit. Testing in a chamber ensures that a device complies with these limits. In Europe, the CE marking signifies that a product meets the necessary EMC requirements. Testing in an EMC chamber is a key step in achieving this certification.
The Impact of Non-Compliance
If a device does not pass EMC testing, it may not be allowed to enter certain markets or regions. Non-compliance can also lead to operational issues, as devices that emit excessive electromagnetic interference can disrupt critical systems, from communication networks to medical equipment.
For example, a device that fails to meet EMC standards may cause problems like:
-
Poor performance of nearby electronics.
-
Interference with communication systems.
-
Risk of malfunction in mission-critical equipment, like medical devices or industrial machines.
The Role of EMC Chambers in Consumer Safety
Although chambers are primarily used for compliance testing, they also play a significant role in ensuring consumer safety. By testing for both emissions and immunity, EMC chambers help guarantee that a device will operate safely in environments where it may be exposed to electromagnetic waves from other devices. The presence of an EMC mark (FCC or CE) indicates that the device has been tested for electromagnetic compatibility and is safe to use in a shared electromagnetic environment.
Conclusion: Why EMC Chambers Are Vital for the Electronics Industry
An EMC chamber is a crucial facility in the development of electronic devices. EMC testing helps prevent interference that could negatively affect other devices or critical systems by ensuring that devices meet regulatory standards for emissions and immunity. Whether it's ensuring the stability of a Wi-Fi network, the safety of a medical device, or the clarity of a television signal, chambers play an essential role in maintaining the integrity of modern electronics.
Moreover, as electronic devices continue to proliferate across industries, the importance of EMC testing only grows. With tighter regulations and greater consumer expectations for device reliability, having access to a well-equipped EMC test chamber is more important than ever.
In conclusion, EMC chambers are integral to the modern electronics industry. By ensuring that products comply with EMC standards, these chambers help facilitate the safe and effective integration of electronic devices into our everyday lives.
Looking for high-quality RF absorbers? Browse our in-stock pyramidal absorbers — shipping from California in 1-2 business days.
This article was written by the RF engineering experts at dB Absorber, specialists in high-performance microwave and RF absorbing solutions.